Population surveys of various countries show that 2-10% of adult men experience symptoms that indicate problems with the prostate throughout their lives.
Any urinary disturbance is a wake-up call, and self-treatment in this case should be ruled out. However, the problem is not always associated with prostatitis.
See a doctor
Our articles are written with a passion for evidence -based medicine. We refer to reputable sources and seek comments from reputable physicians. But remember: the responsibility for your health lies with you and your doctor. We don't write prescriptions, we make backups. It is up to you to rely on our views or not.
How the prostate works
The prostate, or prostate gland, is a walnut -like organ located just below the bladder. Between the parts of the "nut" passes the urethra - the tube through which urine is expelled from the bladder, and sperm from the testicles.
The main task of the prostateconsists in the secretory production of which is part of the semen. Thanks to this secret, sperm can move. The second task of the prostate is to contract, enabling ejaculation, i. e. ejaculation.
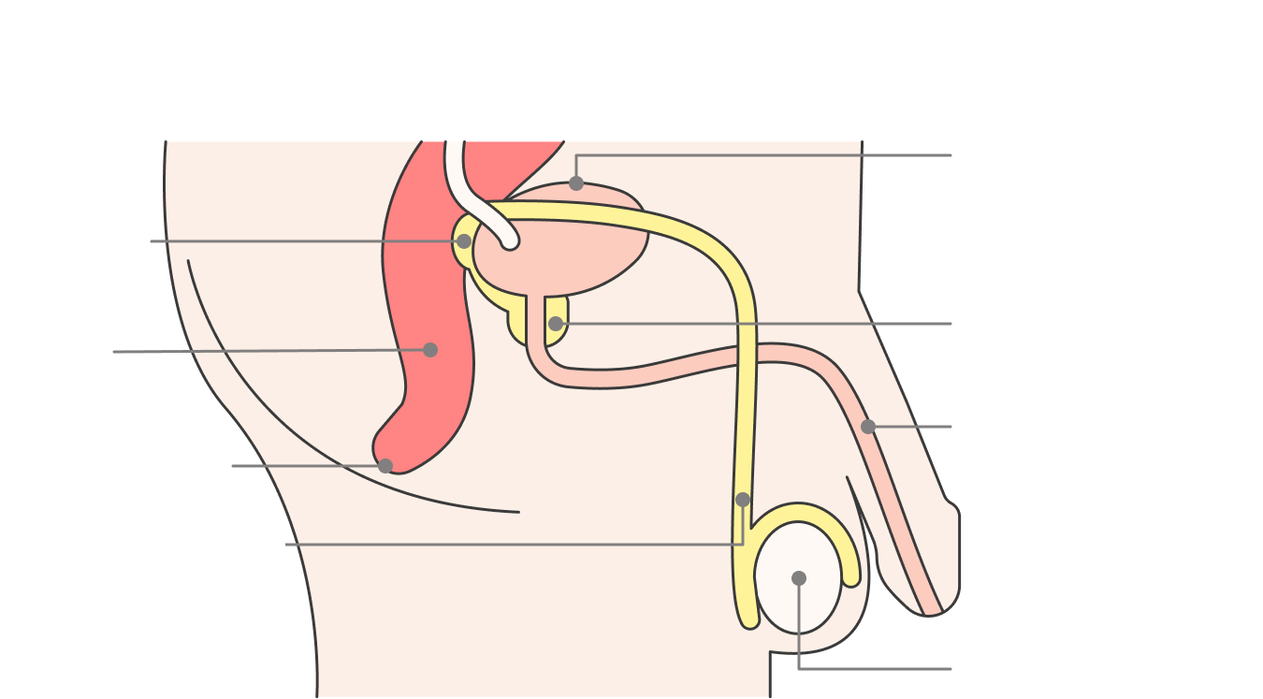
Next to the prostate there is a seminal vesicle connected to the vas deferens, where the sperm leave the genitals. The seminal vesicles produce a portion of semen fluid and store prostate secretions.
The secretion of the prostate is a mixture of citric acid and enzymes. This fluid dilutes the semen, which flows into the urethra from the testis vas deferens.
Prostate problems do not always lead to erection problems
In most cases, sexual dysfunction is not related to problems with the prostate, as there is no physical connection between the prostate and the mechanism of erection.
But difficulty urinating, discomfort due to incomplete emptying of the bladder, pain or discomfort associated with inflammation, cause a person to begin to feel nervous and embarrassed. Therefore, psychological problems arise - as a rule, they are problems that negatively affect erections.
What is prostatitis
Prostatitis is an inflammation of the prostate gland associated with pathogenic microbes or other non -infectious causes. Sometimes inflammation also affects the seminal vesicles - this is called vesiculitis.
At the same time, inflammation of the prostate gland does not always cause pain and problems with urination, and the presence of unpleasant symptoms is not necessarily associated with inflammation of the gland.
To avoid confusion, urologists around the world use the classification recommended by the American National Institute for the Study of Diabetes Mellitus, Digestive and Kidney Diseases, or NIDDK.
To simplify a bit, the classification divides prostatitis into bacterial and bacterial, which are not related to bacteria. This approach helps doctors make important decisions - whether to prescribe antibiotics and additional medications. Giving antibiotics to all patients with suspected prostatitis is wrong because non -microbial forms of prostatitis are more common than bacterial. Taking unnecessary antibiotics is not good for your health.
The NIDDK classification identifies five forms of prostatitis.
Acute bacterial prostatitis.The disease is most often caused by special pathogens of urinary tract infections: for example, E. coli, Klebsiella and Enterobacter.
As a rule, the disease begins unexpectedly and is accompanied by a deterioration of general well -being. Temperatures rise to 38-39 ° C, with some people feeling weak, severe pain or burning in the perineum, scrotum or anus, in the lower abdomen, and sometimes in the muscles. Some people experience pain during ejaculation. Sometimes with bacterial prostatitis, there is frequent, difficult, and painful urination.
Chronic bacterial prostatitis.The disease can also be caused by special microbes of acute prostatitis. The disease is considered chronic if symptoms last for at least three months.
The symptoms of chronic bacterial prostatitis are similar to acute, but may be less severe or less severe. Fever and weakness are usually absent, the pain in the lower abdomen is more painful than sharp, but it is difficult to urinate and empty the bladder completely. Moreover, the unpleasant symptoms may disappear temporarily and, after a while, reappear.
Any man can get sick with acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis. But those most at risk are those who have a higher risk of contracting germs: those who have sex, especially anal sex, without condoms, patients with urinary tract infections, and people who have just had surgery or a prostate biopsy.
Chronic abacterial prostatitis associated with inflammation.The symptoms of inflammatory non -bacterial prostatitis are very similar to those of acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis. At the same time, there are no pathogenic bacteria in semen, prostate skeleton and urine, but the concentration of leukocytes will be high - this indicates inflammation of the prostate gland.
Chronic abacterial prostatitis, or chronic pelvic pain syndrome, is not associated with inflammation.The symptoms also mimic acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis. At the same time, there are no pathogenic bacteria and high concentrations of leukocytes in semen, prostate skeleton and urine - this indicates that the prostate gland is not inflamed.
In the case of non -bacterial prostatitis, it is impossible to know what causes the development of the disease. Risk groups are also difficult to determine.
Asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis.This form of the disease does not cause discomfort. Often, inflammation is discovered by chance while a patient is being examined for other problems, such as infertility.
How does prostatitis differ from prostate adenoma
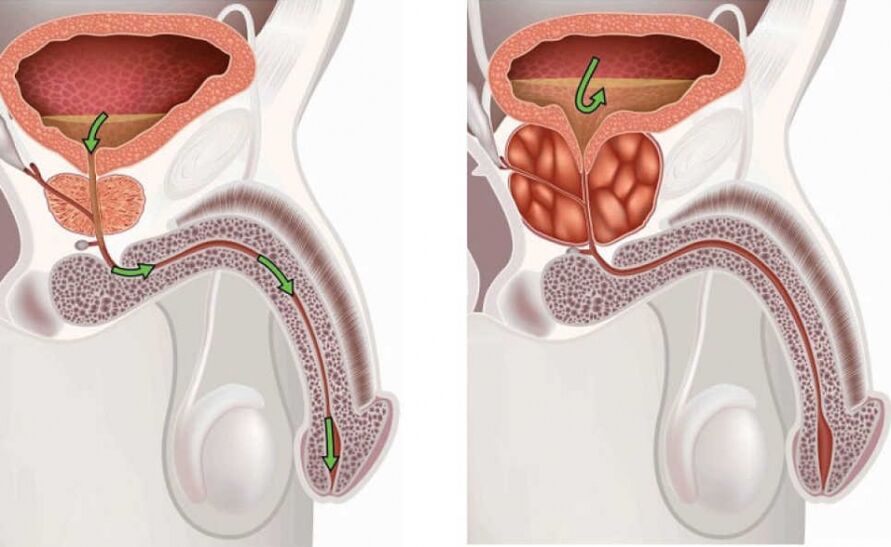
In about 8% of men after the age of 40, the prostate begins to enlarge - this is called prostate adenoma, or benign prostatic hyperplasia. The prostate is too much blocking the urethra, and because of this, problems with urination can begin: too frequent urge to use the toilet or leakage of urine. When faced with the symptoms of an adenoma, some patients may assume that they have prostatitis.
Although some symptoms of prostate hyperplasia may resemble prostatitis, they are not the same thing. Prostatitis is an inflammation of the prostate gland. And adenomas are age -related uncontrolled proliferation of prostate cells that are not associated with inflammation.
Adenomas can cause serious discomfort, so if you have trouble urinating, it is important to see a urologist as soon as possible. However, adenomas are still as harmless as prostatitis, as they do not increase the risk of cancer.
How Often is Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis Diagnosed?
According to data of the general literature, worldwide, acute bacterial prostatitis occurs in 5-10% of cases, and chronic bacterial prostatitis-in 6-10% of cases. Moreover, both variants of chronic abacterial prostatitis account for 80–90% of all cases of the disease.
If we do a massive microscopic examination of the prostate gland, we will find certain signs of inflammation in all men without exception after 40 years. But it has nothing to do with the diagnosis of chronic bacterial prostatitis.
There are many urological diseases that can hide behind the mask of chronic prostatitis, some of which are quite serious and require immediate treatment. Therefore, I recommend that all patients with symptoms resembling prostatitis undergo a more detailed examination, which will clarify their diagnosis.
How is prostatitis diagnosed?
From the patient’s point of view, the symptoms of bacterial and non -bacterial prostatitis are very similar. Without consulting a urologist and special tests, it is impossible to distinguish one form of prostatitis from another and get quality treatment. You can get an appointment with a urologist for free under a compulsory medical insurance policy or make an appointment with a doctor at a private clinic.
The main task of the urologist, who discovers patients with suspected prostatitis, is to exclude other prostate diseases, for example, cancer, and to determine the form of the disease a person is suffering from. It is very important to distinguish chronic pelvic pain syndrome from bacterial prostatitis with confirmed or suspected pathogens. This is what doctors need to do to deal with it.
Ask the patient about symptoms and well -being.To gather more information, your doctor may suggest answering a question from a questionnaire called the Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index. In some cases, in order not to waste time during an appointment, it makes sense to print out a questionnaire and fill it out first.
Perform a physical examination.The doctor will examine the patient, paying special attention to the groin area. If there is a swollen and painful lymph node in the groin, this will increase the chances of the body being completely inflamed. Typically, these tests include a digital rectal exam, which allows the doctor to assess the size, shape, and condition of the prostate. This study helps to find out if the prostate is enlarged. If the gland is painful to the touch, it is most likely inflamed.
Is it possible to do without a digital rectal examination
Digital rectal exams and prostate massage are not the most pleasant procedures. In acute inflammation, this can be painful. Some patients are so eager to avoid this procedure that, in principle, they refuse to make an appointment with a urologist.
Digital rectal examination is a diagnostic method, but massage of the prostate gland through the rectum is done to obtain material for laboratory analysis - the secret of the prostate gland. If the secretion cannot be obtained, the doctor may replace the analysis of prostate gland secretions with analysis of the first part of the urine, or two- and three -glass urine samples. These studies allow you to roughly determine where the problem area is in the urinary tract.
Sometimes, instead of this examination, semen analysis is prescribed for the same purpose. This helps understand whether prostatitis is part of an infection of the male genital glands and provides information on the quality of ejaculation. In addition, the count of leukocytes in ejaculation makes it possible to distinguish between inflammatory and non -inflammatory forms of chronic pelvic pain syndrome.
If a patient is worried about an upcoming digital examination or prostate massage, I would advise you to discuss it with your doctor. Perhaps analysis of prostate secretions, to obtain that which only requires its sequence, can be replaced with analysis of urine or semen.
Order blood tests, urine secretions and prostate.Diagnostic standards include microscopic examination of prostate gland secretions, general blood tests, general analysis of urine with sediment microscopy, as well as microbiological examination of urine and prostate gland secretions.
During a microbiological study, the patient’s biological material is placed on a nutrient medium and they see what bacteria are growing on it - this allows you to clarify the diagnosis. You can take the test at a private clinic for money or for free under compulsory medical insurance.
Other tests and examinations - such as prostate -specific antigen (PSA) concentrations in the blood and prostate transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) - are usually not performed if prostatitis is suspected. In some cases, prostate TRUS can reveal fibrosis, i. e. scarring, or foci similar to malignant tumors, but such studies have not been shown for all patients without exception.
How is prostatitis treated?
Treatment depends on the type of prostatitis. If the inflammation is provoked by bacteria, the doctor will choose antibiotics. And if the bacteria has nothing to do with it, medications will be needed to help overcome the unpleasant symptoms of the disease.
Acute bacterial prostatitisstart treatment without waiting for test results - this is called empirical antibiotic therapy. With this approach, antibiotics are prescribed based on knowledge of which germs are most likely to cause prostate infections.
As a rule, patients are prescribed antibacterial drugs that penetrate into the tissues of the prostate gland and act as the most "popular" causative agents of prostatitis and urinary tract infections.
People who feel more or less normal and are treated at home usually receive antibiotics in pill form. And patients with high fever treated in hospital are more likely to be given antibiotics by injection. With this treatment, in most patients with acute prostatitis, fever and pain are relieved on the second to sixth day after starting medication.
When the patient’s temperature returns to normal, and the signs of inflammation disappear, the doctor can transfer the patient from injection to pill. The total duration of antibiotic treatment is usually around 2-4 weeks.
Sometimes prostate massage is used not only as a diagnostic method, but also as a therapeutic technique. It was once thought that it could help release excess secretions accumulated in the gland and thus reduce its swelling. However, today most experts have agreed that prostate massage should be avoided for bacterial prostatitis. This is not only painful and useless, but can also exacerbate the course of the disease, because as a result of massaging, bacteria can get into nearby tissues and not become infected.
Chronic bacterial prostatitisalso treated with antibiotics that target gram -negative bacteria. For treatment, fluoroquinolones are usually used - these antibiotics are considered quite safe. But if the doctor suspects that other microorganisms have caused prostatitis, he or she can prescribe additional antibacterial drugs without waiting for the test results.
With chronic prostatitis, antibiotics need to be taken longer than with acute ones. In accordance with the recommendations of urologists, they are prescribed within 4-6 weeks.
Chronic abacterial prostatitisis not associated with bacteria, so patients with this disease are prescribed antibiotics only if, in addition to prostatitis, they have a urinary tract infection.
Since it is not clear what exactly causes bacterial prostatitis, treatment is primarily aimed at relieving pain when urinating. To do this, doctors prescribe alpha-1-blockers, drugs that help relax the prostate muscles that compress the urethra. If the pain persists, your doctor may prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication. The dose for each patient is selected individually.
Some patients with abacterial prostatitis are assisted by cognitive behavioral therapy - this is the name of a session with psychology, where a person learns to cope with pain without medication. At the same time, there is still no scientific evidence on the effectiveness of psychological assistance for bacterial prostatitis.
Studies in which researchers try to prove the effectiveness of other interventions, such as acupuncture, electromagnetic chair therapy, prostate massage, or transrectal therapy, are not well planned and require little time - usually less than 12 weeks. Therefore, it is impossible to say whether all this helped or not.
How to prevent prostatitis: prevention
The main cause of discomfort in the prostate gland is a sedentary lifestyle and less sex life. Doctors believe that the highest chance of avoiding prostatitis is in men who:
- Have fun having sex regularly.
- They regularly do moderate exercise.
- Avoid hypothermia.
- After reaching the age of 40, they undergo a urological examination every year.
Where better to treat prostatitis - in public or private clinics
The most important thing is the principles of evidence -based medicine followed in the diagnosis and treatment of prostatitis. That just depends on the doctor - and it doesn’t matter where he works.
Unfortunately, doctors in private clinics do not always adhere to standards of medical care. This can lead to too many unnecessary diagnoses and treatments, so patients run the risk of paying more. In state medical organizations, the likelihood of complying with all standards of diagnosis and treatment is higher. But patients need to take into account that a complete examination requires more time, sometimes more than during an examination at a private clinic.
Remember
- Problems with the urinary tract in men are common, but do not always occur in prostatitis. To understand what is really going on in a person, you need to undergo a thorough examination.
- Prostate problems rarely cause erectile difficulties. Usually, with prostatitis, it is debilitating due to psychological problems that arise against the background of unpleasant symptoms.
- Not every form of prostatitis is caused by bacteria: in 80-90% they have nothing to do with it. If someone with suspected prostatitis is prescribed antibiotics without additional testing, this is bad. Before taking it, it makes sense to see another doctor.
- A person with acute or chronic prostatitis may be given a prostate massage to collect glandular secretions for analysis.
- The best method of preventing prostatitis is protected sex, a healthy lifestyle, and after 40 years - regular urological examinations by a doctor.































